Water conservation has become an undeniable necessity, especially within the context of Thermal Power Plants (TPPs). This isn’t merely about preserving a precious resource; it’s about adhering to increasingly stringent governmental regulations and ensuring the long-term viability and sustainability of our energy infrastructure. The reality is harsh: TPPs are significant consumers of water, and the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change has set firm limits on water consumption: 3.5 cubic meters per megawatt-hour (M3/MWh) for existing plants and a more restrictive 2.5 M3/MWh for new plants commissioned after January 1st, 2017.
Many power plants, including those operated by governmental entities, rely on freshwater, RO (Reverse Osmosis) permeate, and Sewage Treatment Plant (STP) – treated water. These resources often come at a substantial cost per cubic meter. Furthermore, the elevated chloride content frequently found in these water sources necessitates operating cooling towers at low Cycles of Concentration (COC). This practice leads to a considerable volume of water being discharged as blowdown from the cooling tower systems. Consequently, this increases the overall water demand for cooling towers and imposes a significant financial burden on TPP operations.
The challenges don’t end there. Even when operating at lower COC levels, the risk of hard water scaling within the turbine steam condenser remains a persistent threat. This scaling adversely affects condenser vacuum, leading to increased steam consumption per megawatt of electricity produced and, ultimately, impacting the profitability of the thermal power plant.
The Financial Implications of Water Management
To illustrate the scale of the challenge, consider a 1000 MW power plant. Implementing a conventional RO plant to treat and recover cooling tower blowdown water for reuse requires a minimum capital expenditure (CAPEX) in the range of Rs. 100-125 crore. Beyond this substantial initial investment, there are also significant daily operating costs (OPEX) associated with treating each cubic meter of cooling tower blowdown water.
SCALEBAN: A Sustainable and Innovative Solution
Fortunately, a more innovative, unique, and sustainable approach exists. SCALEBAN technology offers a paradigm shift in how TPPs can reuse ETP (Effluent Treatment Plant)-treated water, cooling tower blowdown, RO reject, and various other wastewater streams. This technology enables cooling tower circuits to operate efficiently at significantly higher COC levels (15-20) compared to the standard COC of 2-3. This dramatic increase results in a substantial reduction in cooling tower blowdown, potentially up to 90% compared to current levels, while simultaneously ensuring the efficient operation of the power plant. Crucially, SCALEBAN eliminates the need for the high CAPEX and OPEX associated with conventional water treatment technologies.
Understanding SCALEBAN Technology
SCALEBAN is a comprehensive system that combines specialized equipment, specialty chemicals, and filtration. It’s designed to handle wastewater within cooling towers even at very high Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) concentrations (25%-30%) and the aforementioned high COC levels (up to 20). The core principle behind SCALEBAN is to convert hardness causing salts like calcium & magnesium into fine colloidal particles, preventing the formation of hard scales at the heat transfer areas. This is achieved without adding any chemicals to the water, making it an environmentally sound solution.
Key Benefits of SCALEBAN for Thermal Power Plants
Optimized Water Efficiency:
- Achieves high Cooling Tower Cycles of Concentration (COC) of 15-20.
- Reduces Cooling Tower blowdown by up to 90%.
- Lowers overall water consumption by 25-30%.
Significant Cost Savings:
- Eliminates the need for high CAPEX and OPEX associated with conventional technologies.
- Offers a fast Return on Investment (ROI), typically within 18 months.
Enhanced Operational Reliability:
- Prevents turbine condenser scaling, ensuring zero downtime.
- Maintains designed condenser vacuum for optimal efficiency.
- Reduces steam consumption per MW of power generation.
- Ensures scale, corrosion, and biofouling-free operation of the entire cooling tower circuit.
Environmental Sustainability:
- Requires minimal energy to operate, resulting in reduced CO2 emissions.
Scaleban Water Conservation Scheme For Thermal Power Plant
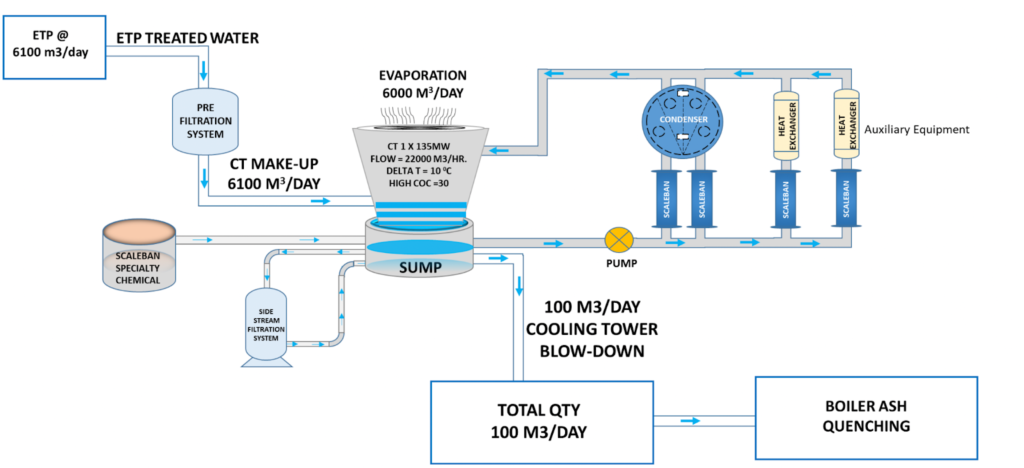
SCALEBAN in Action: Real-World Applications
SCALEBAN technology has been successfully implemented across various industries, demonstrating its versatility and effectiveness. These include power plants, chemical and pharmaceutical facilities, and even distilleries, sugar and ethanol plants. Case studies highlight significant water savings and the achievement of Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) goals.
The Path to a Sustainable Future
SCALEBAN technology represents a paradigm shift in water conservation for thermal power plants. It offers a sustainable solution to the pressing need for responsible water management without imposing prohibitive costs on plant operations. By embracing innovative technologies like SCALEBAN, the power sector can significantly reduce its water footprint, ensuring both environmental responsibility and economic viability.
